#U2122DG3. Bracelet Crossings
Bracelet Crossings
Bessie the cow enjoys arts and crafts. In her free time, she has made NN (1≤N≤501≤N≤50) bracelets, conveniently numbered 1…N1…N. The iith bracelet is painted color ii out of a set of NN different colors. After constructing the bracelets, Bessie placed them on a table for display (which we can think of as the 2D plane). She was careful to arrange the bracelets to satisfy the following three conditions:
- Every bracelet was a single closed polygonal chain -- a series of vertices (points) connected sequentially by line segments, where the first and last points are the same (Feel welcome to consult the wikipedia page for more detail: polygonal chain),
- No bracelet intersected itself (this corresponds to a "simple" polygonal chain); and
- No two bracelets intersected.
Unfortunately, right after Bessie arranged the bracelets in such a careful manner, Farmer John drove by in his tractor, shaking the table and causing the bracelets to shift around and possibly break into multiple (not necessarily closed or simple) polygonal chains! Afterward, Bessie wanted to check whether the three conditions above still held. However, it was dark, so she couldn't see the bracelets anymore.
Fortunately, Bessie had a flashlight. She chose MM (1≤M≤501≤M≤50) vertical lines x=1,x=2,…,x=Mx=1,x=2,…,x=M and for each line, she swept the beam of the flashlight along that line from y=−∞y=−∞ to y=∞y=∞, recording the colors of all bracelets she saw in the order they appeared. Luckily, no beam crossed over any vertex of any polygonal chain or two line segments at the same time. Furthermore, for each beam, every color that appeared appeared exactly twice.
Can you help Bessie use this information to determine whether it is possible that the bracelets still satisfy all three of the conditions above?
INPUT FORMAT (input arrives from the terminal / stdin):
Each input case contains TT sub-cases (1≤T≤501≤T≤50) that must all solved independently to solve the full input case. Consecutive test cases are separated by newlines.The first line of the input contains TT. Each of the TT sub-test cases then follow.
The first line of each sub-test case contains two integers NN and MM. Each sub-test case then contains MM additional lines. For each ii from 11 to MM, the ii-th additional line contains an integer kiki (0≤ki≤2N0≤ki≤2N, kiki even), followed by kiki integers ci1,ci2,…,cikici1,ci2,…,ciki (cij∈**[1,N]cij∈[1,N], every cijcij appears zero or two times). This means that when Bessie swept her flashlight from (i,−∞)(i,−∞) to (i,∞)(i,∞), she encountered the colors ci1**,ci2,…,cikici1,ci2,…,ciki in that order.
OUTPUT FORMAT (print output to the terminal / stdout):
For each sub-test case, print YES if it is possible for the three conditions above to be satisfied. Otherwise, print NO.
SAMPLE INPUT:
5
1 2
2 1 1
2 1 1
1 3
2 1 1
0
2 1 1
2 1
4 1 2 1 2
4 2
6 1 2 2 3 3 1
6 1 2 4 4 2 1
2 2
4 1 1 2 2
4 2 2 1 1
SAMPLE OUTPUT:
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
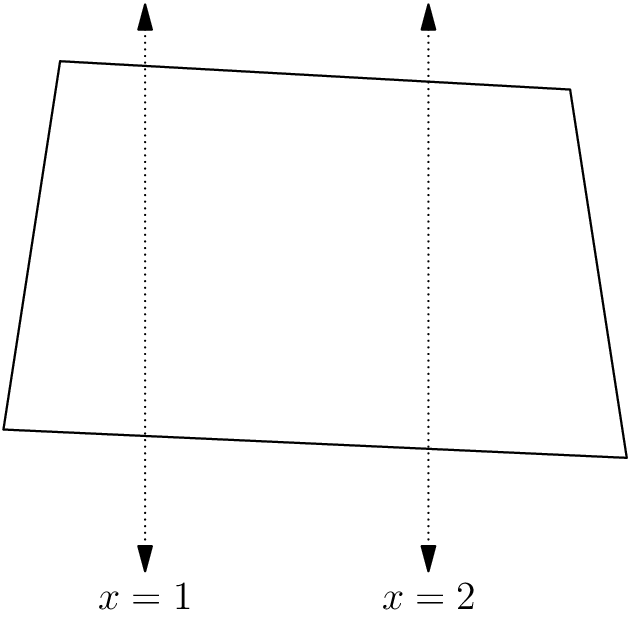
An example of a feasible bracelet configuration for the first sub-case is:
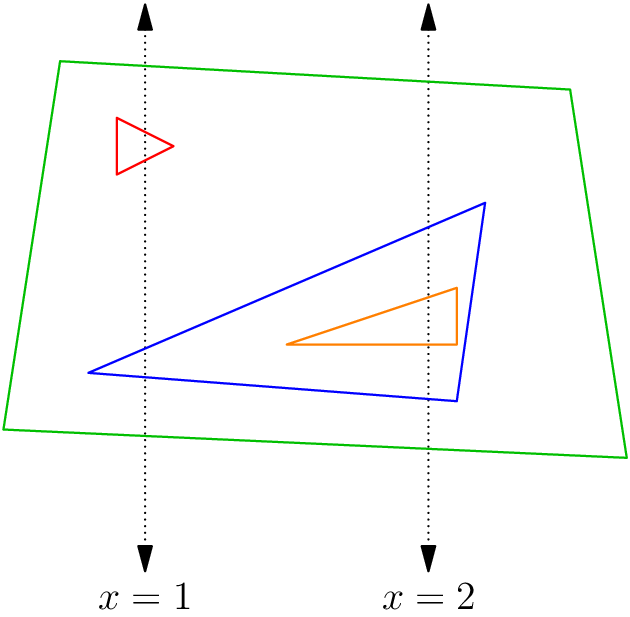
For the fourth sub-case, a feasible arrangement is the following:
SCORING:
- Test case 2 satisfies N=1N=1.
- Test cases 3-5 satisfy N=2N=2.
- Test cases 6-8 satisfy M=1M=1.
- Test cases 9-14 satisfy M=2M=2.
- Test cases 15-20 satisfy no additional constraints.
